The services contracting that the government prefers – Government’s Preferred Service Contracting: Unveiling the Types, Categories, and Strategies for Effective Procurement.
In the realm of public administration, the services contracting that the government prefers has emerged as a crucial aspect of service delivery. This practice offers numerous advantages and entails a well-defined process involving vendor selection, contract management, and oversight. Understanding the government’s preferences in service contracting is essential for both government agencies and potential vendors.
Government Contracting Preferences
The government contracts out a wide range of services to meet its operational needs and fulfill its public service obligations. These services encompass various categories, including:
- Information technology (IT) and telecommunications
- Professional and technical services
- Facilities management
- Transportation
- Healthcare
Numerous government agencies prefer to contract out services, including:
- Department of Defense (DoD)
- Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
- Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)
- General Services Administration (GSA)
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
Contracting out services offers several benefits for government agencies, such as:
- Reduced costs
- Increased efficiency
- Improved access to specialized expertise
- Enhanced flexibility
- Reduced risk
Service Categories and Contract Types: The Services Contracting That The Government Prefers

The government contracts out a diverse array of services, which can be broadly categorized into the following groups:
- Professional and technical services: These include services such as engineering, consulting, research and development, and IT support.
- Facilities management: These services encompass the operation and maintenance of government buildings, grounds, and infrastructure.
- Transportation: These services involve the provision of transportation services, such as bus, rail, and air transportation.
- Healthcare: These services include the provision of medical care, pharmaceuticals, and health insurance.
- Other services: This category includes a wide range of other services, such as food services, janitorial services, and security services.
The government uses various types of contracts to procure services, including:
- Fixed-price contracts: These contracts specify a fixed price for the services to be provided, regardless of the actual costs incurred by the contractor.
- Cost-reimbursement contracts: These contracts reimburse the contractor for the actual costs incurred, plus a fixed fee or percentage.
- Time-and-materials contracts: These contracts pay the contractor for the time and materials used to perform the services.
- Indefinite-delivery/indefinite-quantity (IDIQ) contracts: These contracts establish a framework for the government to purchase services on an as-needed basis.
| Contract Type | Description | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed-price | Specifies a fixed price for services | Low risk for government, high risk for contractor |
| Cost-reimbursement | Reimburses contractor for actual costs plus fee | High risk for government, low risk for contractor |
| Time-and-materials | Pays contractor for time and materials used | Moderate risk for both government and contractor |
| IDIQ | Establishes framework for government to purchase services as needed | Flexibility for both government and contractor |
Vendor Selection and Evaluation Criteria
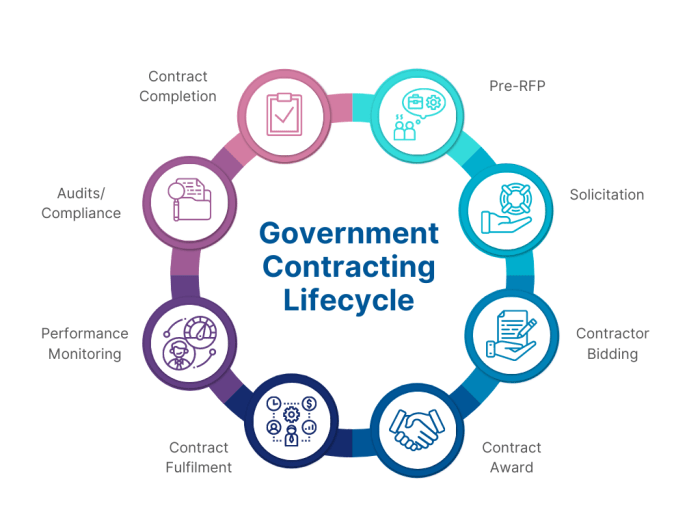
The government uses a rigorous process to select vendors for its contracts. This process typically involves the following steps:
- Solicitation: The government issues a solicitation document that describes the services required and the evaluation criteria that will be used to select the vendor.
- Proposal submission: Vendors submit proposals that describe their qualifications and how they will meet the government’s requirements.
- Evaluation: The government evaluates the proposals based on the evaluation criteria specified in the solicitation.
- Selection: The government selects the vendor that offers the best value to the government.
- Technical qualifications: The vendor’s experience, expertise, and ability to perform the services.
- Past performance: The vendor’s track record of successfully completing similar projects.
- Price: The cost of the vendor’s services.
- Small business status: The government gives preference to small businesses in its contracting process.
- Submitting a well-written proposal that clearly demonstrates their qualifications and how they will meet the government’s requirements.
- Providing strong references from previous clients.
- Offering competitive pricing.
- Attending government contracting workshops and seminars.
- Monitoring the vendor’s performance: The government monitors the vendor’s performance to ensure that the services are being provided in accordance with the contract.
- Enforcing the contract: The government has the right to enforce the contract if the vendor fails to meet its obligations.
- Modifying the contract: The government may modify the contract if there is a change in the scope of work or the government’s needs.
- Terminating the contract: The government may terminate the contract if the vendor fails to meet its obligations or if the government no longer needs the services.
- Cost overruns: The vendor may charge more than the agreed-upon price for the services.
- Delays: The vendor may not be able to complete the services on time.
- Poor quality: The vendor may not provide the services to the required quality standards.
- Fraud: The vendor may engage in fraudulent activities, such as overcharging the government or providing inferior services.
- Selecting vendors carefully: The government should select vendors with a proven track record of success and who are financially sound.
- Negotiating clear and concise contracts: The government should negotiate contracts that clearly define the scope of work, the price, and the performance standards.
- Monitoring vendor performance closely: The government should monitor vendor performance closely to ensure that the services are being provided in accordance with the contract.
- Enforcing the contract: The government should not hesitate to enforce the contract if the vendor fails to meet its obligations.
- The use of technology: The government is increasingly using technology to streamline the contracting process and improve the efficiency of its contracts.
- The focus on small businesses: The government is giving more preference to small businesses in its contracting process.
- The emphasis on performance-based contracting: The government is increasingly using performance-based contracts, which tie payments to the vendor’s performance.
- The development of new contracting models: The government is developing new contracting models, such as the public-private partnership (PPP) model, to meet its changing needs.
The government uses a variety of evaluation criteria to assess vendor proposals, including:
Vendors can improve their chances of winning government contracts by:
Contract Management and Oversight

Once a contract has been awarded, the government is responsible for managing and overseeing the contract to ensure that the vendor is meeting the terms of the contract. This includes:
Contract management is a complex and challenging process. The government faces a number of risks when it contracts out services, including:
The government can mitigate these risks by:
Trends and Innovations in Government Contracting
The government contracting landscape is constantly evolving. Some of the emerging trends and innovations include:
These trends and innovations are having a significant impact on the government contracting process. The government is becoming more efficient, more focused on small businesses, and more performance-oriented. These changes are likely to continue in the future, as the government seeks to improve the way it procures services.
Answers to Common Questions
What types of services does the government prefer to contract out?
The government prefers to contract out a wide range of services, including information technology, professional services, construction, and facilities management.
What are the benefits of contracting out services for government agencies?
Contracting out services can provide government agencies with cost savings, increased efficiency, access to specialized expertise, and reduced administrative burden.
How does the government select vendors for contracts?
The government uses a competitive bidding process to select vendors for contracts. Vendors must submit proposals that demonstrate their qualifications and experience.