Venn diagram for prokaryotic and eukaryotic – Venn diagrams, powerful tools for visualizing relationships between sets, offer invaluable insights into the striking similarities and profound differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. This comparative analysis unveils fundamental principles governing cellular evolution, diversity, and potential therapeutic targets.
Prokaryotic cells, simpler and smaller, lack a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Eukaryotic cells, larger and more complex, possess a nucleus and an array of membrane-bound organelles. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for grasping the intricate tapestry of life.
Venn Diagrams: A Tool for Comparing Sets
Venn diagrams are graphical representations that illustrate the relationships between different sets. They are commonly used to compare and contrast the similarities and differences between two or more sets.
A simple Venn diagram consists of two overlapping circles, where the overlapping region represents the elements that are common to both sets. The areas outside the overlap represent the elements that are unique to each set.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Venn Diagram For Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic
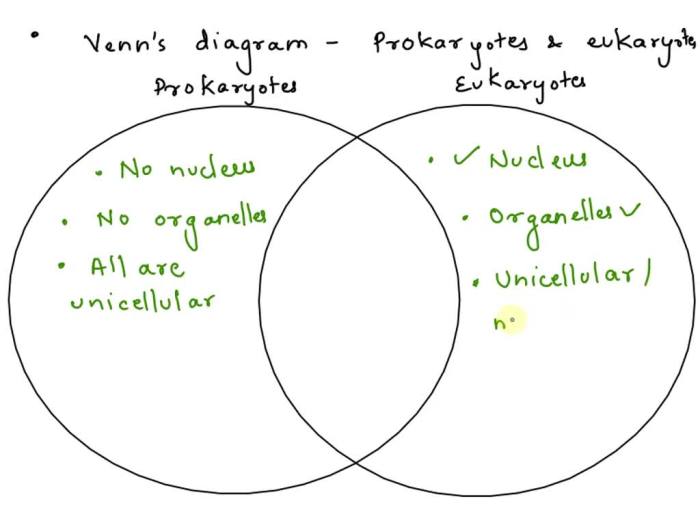
Cells are the fundamental units of life. They can be classified into two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic cellsare simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells. They lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
- Eukaryotic cellsare more complex and larger than prokaryotic cells. They have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Major Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, Venn diagram for prokaryotic and eukaryotic
- Size:Prokaryotic cells are typically 1-10 micrometers in size, while eukaryotic cells are typically 10-100 micrometers in size.
- Nucleus:Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains the cell’s genetic material.
- Membrane-bound organelles:Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a variety of membrane-bound organelles, including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus.
- Ribosomes:Prokaryotic cells have smaller ribosomes (70S), while eukaryotic cells have larger ribosomes (80S).
Venn Diagram for Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
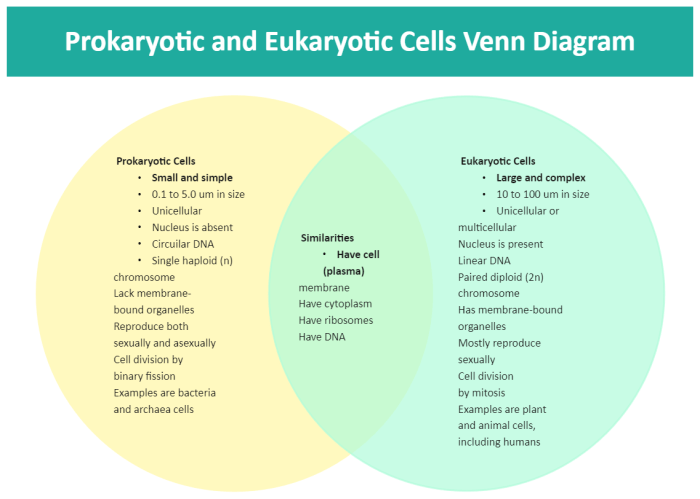
The Venn diagram below illustrates the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Common features:Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes.
- Unique features of prokaryotic cells:Prokaryotic cells have a single, circular chromosome, lack membrane-bound organelles, and have smaller ribosomes.
- Unique features of eukaryotic cells:Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and larger ribosomes.
Analysis of the Venn Diagram

The Venn diagram provides a clear and concise overview of the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
The diagram can be used to identify potential targets for antibiotic therapies. For example, antibiotics that target the unique features of prokaryotic cells would not be effective against eukaryotic cells.
The diagram can also be used to explore other applications in the study of cell biology, such as understanding the evolution and diversity of cells.
FAQ Guide
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess both.
How does the Venn diagram help us understand the evolution of cells?
The diagram reveals shared features that suggest a common ancestor and unique features that reflect divergent evolutionary paths.