Embark on a scientific journey with the law of conservation of matter worksheet answer key, a comprehensive guide that unravels the fundamental principle that matter can neither be created nor destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. Join us as we delve into the depths of this foundational concept, exploring its historical roots, practical applications, and limitations, all while equipping you with the knowledge to master your worksheet questions with confidence.
This meticulously crafted resource provides a roadmap to understanding the behavior of matter, empowering you to grasp the essence of chemical transformations and the conservation of mass and energy in closed systems. Prepare to unlock the secrets of matter and its unwavering nature.
Matter and Its Properties
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. It is composed of atoms and molecules, which are the fundamental building blocks of all substances. Matter exists in three main states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape, and gases have no definite shape or volume.
Physical changes are changes in the form or appearance of a substance without changing its chemical composition. Examples of physical changes include melting, freezing, boiling, sublimation, and condensation. Chemical changes are changes in the chemical composition of a substance. Examples of chemical changes include burning, rusting, and cooking.
Law of Conservation of Matter
The law of conservation of matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. This means that the total amount of matter in a closed system remains constant, regardless of the changes that occur within the system.
The law of conservation of matter was first proposed by Antoine Lavoisier in the 18th century. Lavoisier conducted a series of experiments in which he showed that the mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction is equal to the mass of the products.
This led him to conclude that matter cannot be created or destroyed.
Applications of the Law
The law of conservation of matter has a wide range of applications in chemistry, physics, and engineering. In chemistry, the law is used to balance chemical equations and predict the products of a reaction. In physics, the law is used to explain the conservation of mass and energy in closed systems.
In engineering, the law is used to design and operate chemical reactors and other systems that involve the transfer of matter.
Limitations and Exceptions
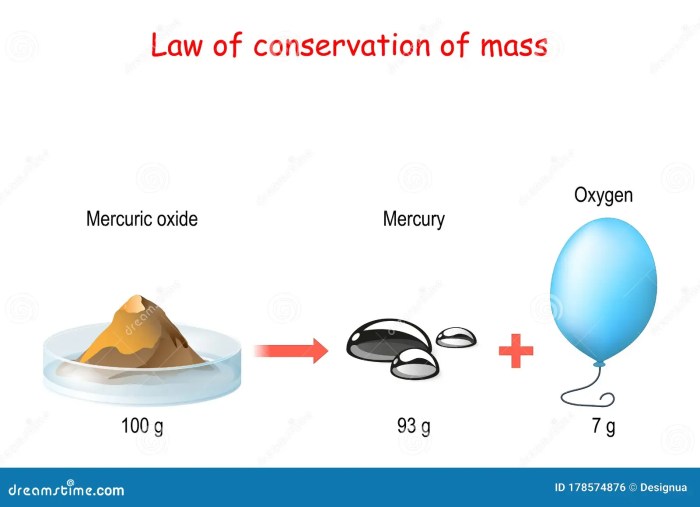
The law of conservation of matter is a general law that applies to most chemical reactions. However, there are some exceptions to the law. For example, the law does not apply to nuclear reactions, which involve the conversion of mass into energy.
The law also does not apply to special relativity, which predicts that mass can be created or destroyed under certain conditions.
Worksheet Answer Key: Law Of Conservation Of Matter Worksheet Answer Key

| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| What is matter? | Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. | Matter is composed of atoms and molecules, which are the fundamental building blocks of all substances. |
| What are the three main states of matter? | Solid, liquid, and gas | Solids have a definite shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape, and gases have no definite shape or volume. |
| What is the law of conservation of matter? | Matter cannot be created or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. | This means that the total amount of matter in a closed system remains constant, regardless of the changes that occur within the system. |
| Who first proposed the law of conservation of matter? | Antoine Lavoisier | Lavoisier conducted a series of experiments in the 18th century that led him to conclude that matter cannot be created or destroyed. |
| What are some applications of the law of conservation of matter? | Balancing chemical equations, predicting the products of a reaction, explaining the conservation of mass and energy in closed systems, and designing and operating chemical reactors. | The law of conservation of matter is a fundamental law that has a wide range of applications in science and engineering. |
FAQ Insights
What is the law of conservation of matter?
The law of conservation of matter states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. The total mass of reactants and products remains constant throughout a chemical change.
How is the law of conservation of matter applied in balancing chemical equations?
By ensuring that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation, the law of conservation of matter helps balance chemical equations. This ensures that mass is conserved throughout the reaction.
What are the limitations of the law of conservation of matter?
The law of conservation of matter does not apply to nuclear reactions, where mass can be converted into energy and vice versa. Additionally, in special relativity, mass can increase with velocity, which also violates the law.