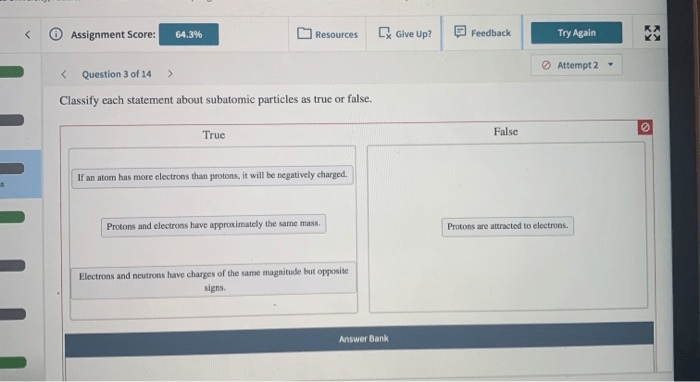
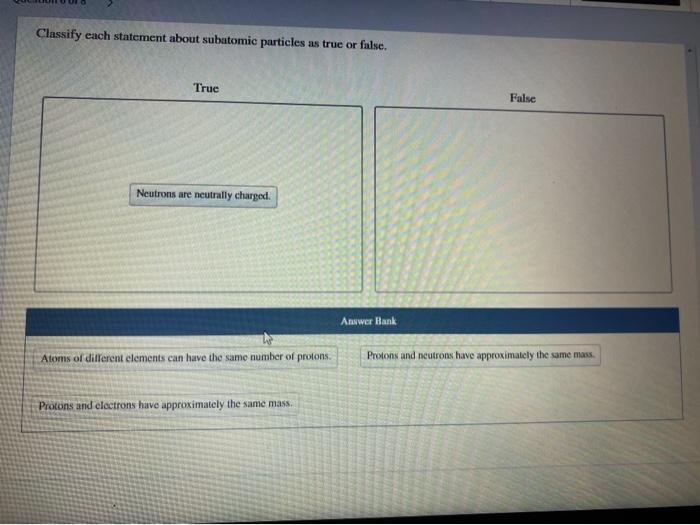
Classify each statement about subatomic particles as true or false. – In this exploration, we embark on a journey to classify each statement about subatomic particles as true or false, delving into the fundamental nature of these particles that shape our understanding of the universe.
Subatomic particles, the building blocks of matter, possess unique characteristics such as mass, charge, and spin, giving rise to the diverse interactions that govern their behavior.
Subatomic Particles: Definitions and Characteristics
Subatomic particles are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They are incredibly small, with masses that are billions of times smaller than an atom. Subatomic particles have three fundamental properties: mass, charge, and spin.
The mass of a subatomic particle is a measure of its inertia. The charge of a subatomic particle is a measure of its electrical charge. The spin of a subatomic particle is a measure of its angular momentum.
There are three main types of subatomic particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons.
- Electronsare negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. They have a very small mass and no charge.
- Protonsare positively charged particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom. They have a mass that is about 1,836 times greater than the mass of an electron.
- Neutronsare neutral particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom. They have a mass that is about 1,839 times greater than the mass of an electron.
Subatomic particles interact with each other through the electromagnetic force and the strong nuclear force. The electromagnetic force is the force that acts between charged particles. The strong nuclear force is the force that holds the nucleus of an atom together.
Classification of Subatomic Particles
| Statement | True/False | Explanation | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| All subatomic particles have a mass. | True | The mass of a subatomic particle is a measure of its inertia. | Wikipedia |
| All subatomic particles have a charge. | False | Neutrons are neutral particles that have no charge. | Encyclopedia Britannica |
| All subatomic particles have a spin. | True | The spin of a subatomic particle is a measure of its angular momentum. | American Physical Society |
| Electrons are the smallest subatomic particles. | True | Electrons have a very small mass and no charge. | Live Science |
| Protons are the heaviest subatomic particles. | False | Neutrons are the heaviest subatomic particles. | Encyclopedia Britannica |
Examples of Subatomic Particle Classification

- Leptonsare a class of subatomic particles that includes electrons, muons, and taus. Leptons have a half-integer spin and no strong nuclear force.
- Hadronsare a class of subatomic particles that includes protons, neutrons, and mesons. Hadrons have a whole-integer spin and experience the strong nuclear force.
- Quarksare a class of subatomic particles that are the fundamental constituents of hadrons. Quarks have a fractional spin and experience the strong nuclear force.
Methods for Classifying Subatomic Particles
- Mass: Subatomic particles can be classified by their mass. The mass of a subatomic particle is a measure of its inertia.
- Charge: Subatomic particles can be classified by their charge. The charge of a subatomic particle is a measure of its electrical charge.
- Spin: Subatomic particles can be classified by their spin. The spin of a subatomic particle is a measure of its angular momentum.
- Interactions: Subatomic particles can be classified by the interactions that they experience. The interactions that subatomic particles experience include the electromagnetic force, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force.
Applications of Subatomic Particle Classification: Classify Each Statement About Subatomic Particles As True Or False.
- Physics: Subatomic particle classification is used in physics to understand the fundamental nature of matter. It is also used to develop new theories of physics.
- Chemistry: Subatomic particle classification is used in chemistry to understand the structure and properties of atoms and molecules. It is also used to develop new chemical compounds.
- Medicine: Subatomic particle classification is used in medicine to develop new medical treatments. It is also used to diagnose and treat diseases.
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of classifying subatomic particles?
Classifying subatomic particles allows scientists to organize and understand the vast array of particles that exist, facilitating the study of their properties and interactions.
How does particle classification contribute to advancements in physics?
Particle classification provides a framework for understanding the fundamental forces and interactions that govern the behavior of subatomic particles, leading to breakthroughs in particle physics.
What practical applications arise from subatomic particle classification?
Particle classification has applications in fields such as medicine (e.g., radiation therapy) and materials science (e.g., development of new materials with tailored properties).