Cellular respiration breaking down energy worksheet – Embark on a journey into the realm of cellular respiration with our engaging worksheet, “Cellular Respiration Breaking Down Energy.” This meticulously crafted resource delves into the intricacies of energy production within living cells, providing a comprehensive understanding of the key processes involved in this vital biological function.
Through a captivating exploration of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, this worksheet unravels the mechanisms by which cells convert nutrients into usable energy. It illuminates the role of enzymes, identifies key products, and unravels the intricate regulation of cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration Overview
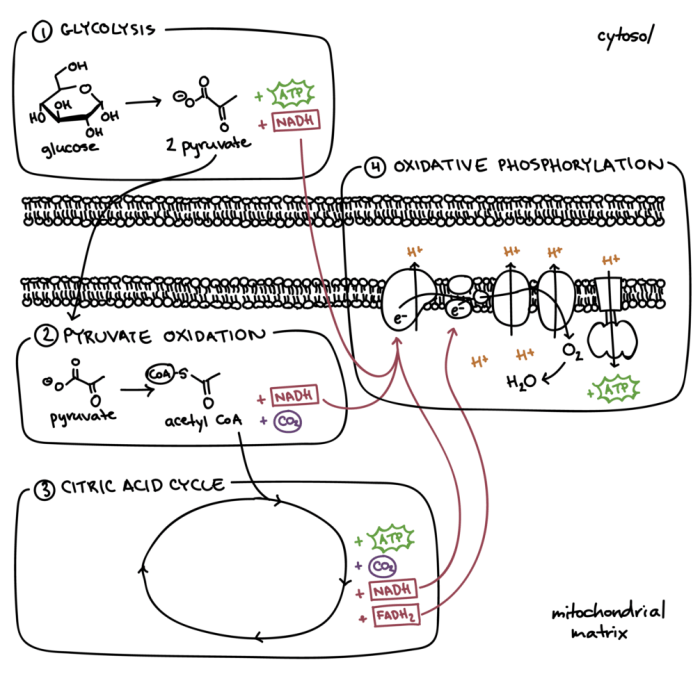
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. This process is essential for the survival of all living organisms because ATP serves as the main energy currency for cells.
Glycolysis
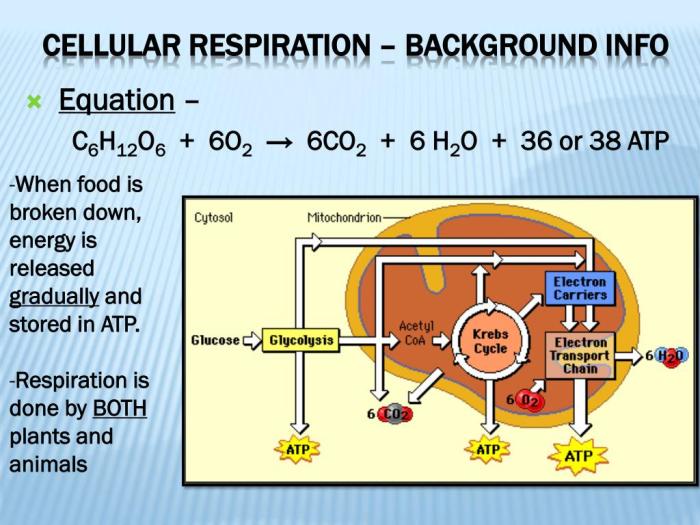
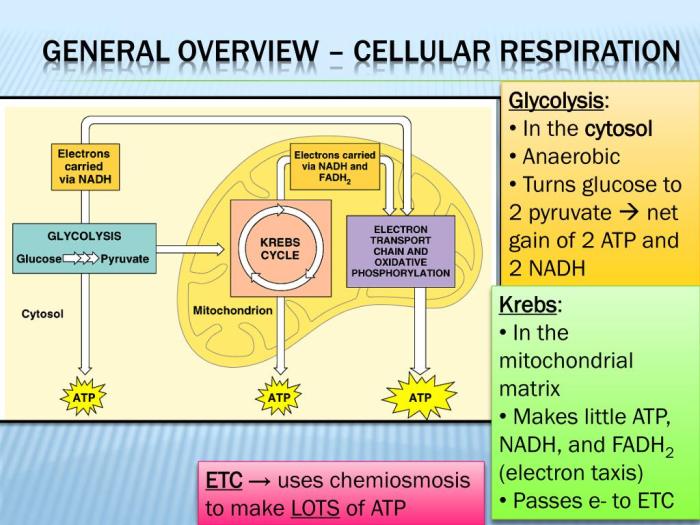
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It involves the breakdown of glucose, a six-carbon sugar molecule, into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon molecule. This process releases a small amount of ATP and produces NADH, a high-energy electron carrier.
Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. It involves the oxidation of pyruvate molecules produced in glycolysis. During this process, carbon dioxide is released as a waste product, and NADH and FADH2, two other high-energy electron carriers, are produced.
Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. It involves the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, which is the final electron acceptor. As electrons pass through the chain, their energy is used to pump protons across the membrane, creating a proton gradient.
This gradient is then used by ATP synthase to generate ATP.
Regulation of Cellular Respiration: Cellular Respiration Breaking Down Energy Worksheet
Cellular respiration is a tightly regulated process that is controlled by various factors, including the availability of oxygen, the levels of ATP, and the presence of certain hormones. When oxygen is present, aerobic respiration occurs, which is a more efficient process that produces more ATP.
In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration takes place, which is a less efficient process that produces less ATP.
User Queries
What is the primary role of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP, the primary energy currency of cells.
What are the key steps of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration involves three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
How is cellular respiration regulated?
Cellular respiration is tightly regulated to ensure efficient energy production and prevent overproduction of ATP.